
extreme mood changes or behavior changes.issues with your vision, hearing, or speech.loss of motor coordination, such as trouble walking.General brain tumor symptoms may include: inability to move or feel a part of the bodyīrain tumor symptoms depend on the size, location, and type of tumor.Symptoms tend to come on suddenly and include: extreme mood changes or unusual behavior.trouble remembering things or difficulty concentrating.sensory problems, such as blurry vision or a ringing in your ears.General brain injury symptoms may include: While they sometimes appear immediately after a traumatic event, they can also show up hours or days later. Brain injury symptomsīrain injury symptoms depend on the type and severity of the injury.
THE BRAIN STEM CONSISTS OF THE HOW TO
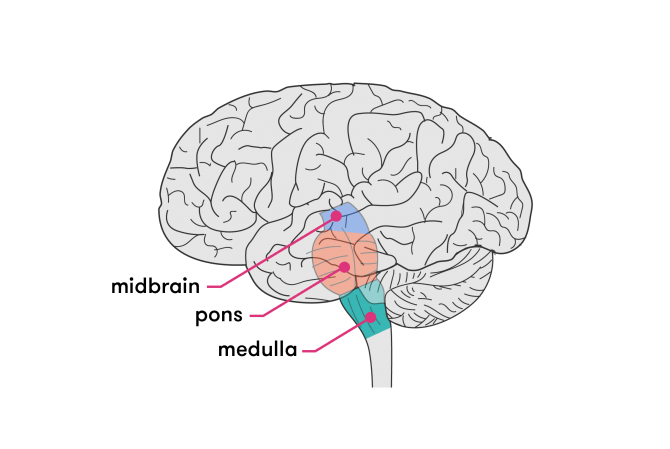
The brain is one of your most important body parts, so it’s important to know how to recognize signs that there may be a problem. It helps regulate many important functions, including motor and sensory functions, breathing, sneezing, and swallowing. It also acts as the control center for the function of the heart and lungs. It acts as the connection between the brain stem and spinal cord. The medulla oblongata is the lowest part of the brain. These nerves are involved in facial movements and transmitting sensory information, as well as breathing.
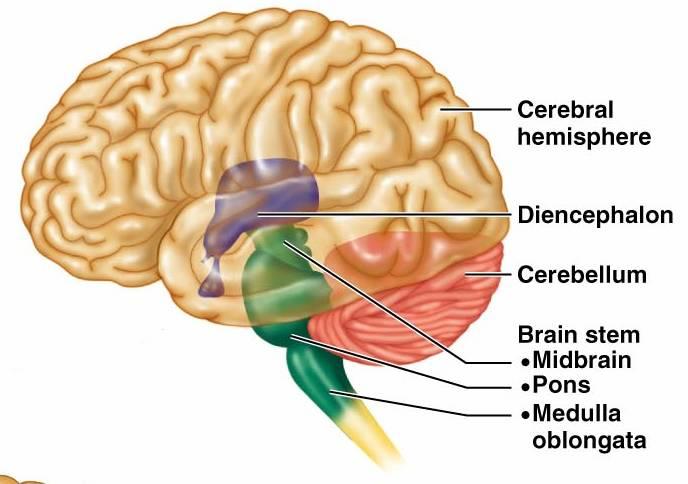
The pons also contains the start of some of the cranial nerves. It’s a group of nerves that help connect different parts of the brain. This is the largest part of the brain stem. The midbrain helps control eye movement, processes visual and auditory information, regulates motor movements, and is involved in arousal and wakefulness. It’s responsible for passing messages to various parts of the body and the cerebral cortex. The brain stem is located in front of the cerebellum and connects to the spinal cord.
controlling the production and release of hormones. maintaining daily physiological cycles, such as the sleep-wake cycle. Some specific actions the hypothalamus is responsible for include: Its role includes controlling eating, sleeping, and sexual behavior. The hypothalamus processes information that comes from the autonomic nervous system. The limbic system is a part of the brain that’s involved with emotion. The epithalamus serves as a connection between the limbic system and other parts of the brain. It’s also involved in alertness, pain sensations, and attention. The thalamus acts as a kind of relay station for signals coming into the brain. The diencephalon is located at the base of the brain. The cerebellum also helps the body maintain its posture, equilibrium, and balance. It’s involved with fine motor skills, which refers to the coordination of smaller, or finer, movements, especially those involving the hands and feet. The cerebellum is located in the back of the brain, just below the occipital lobes. They’re heavily involved in the ability to read and recognize colors and shapes. The occipital lobes are located in the back of the brain. They coordinate specific functions, including hearing, visual memory (such as facial recognition), verbal memory (such as understanding language), and interpreting the emotions and reactions of others. They are located on either side of the head on the same level as the ears. The temporal lobes house the auditory cortex. They’re involved in organizing and interpreting sensory information from other parts of the brain. The parietal lobes are located behind the frontal lobes. The frontal lobes also manage emotions, personality, and temper. They coordinates high-level behaviors, such as motor skills, problem-solving, judgment, planning, and attention. As indicated by their name, they’re located in the front part of the brain. The frontal lobes are the largest of the lobes. Each lobe is associated with different functions: The corpus callosum connects the two hemispheres, thus allowing the brain to deliver messages from one side to the other.Įach hemisphere of the cerebrum is divided into broad regions called lobes. The two hemispheres are separated by a groove called the great longitudinal fissure. It’s divided into two halves, called hemispheres. The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
